PCB Design Guidelines for Manufacturing (DFM)
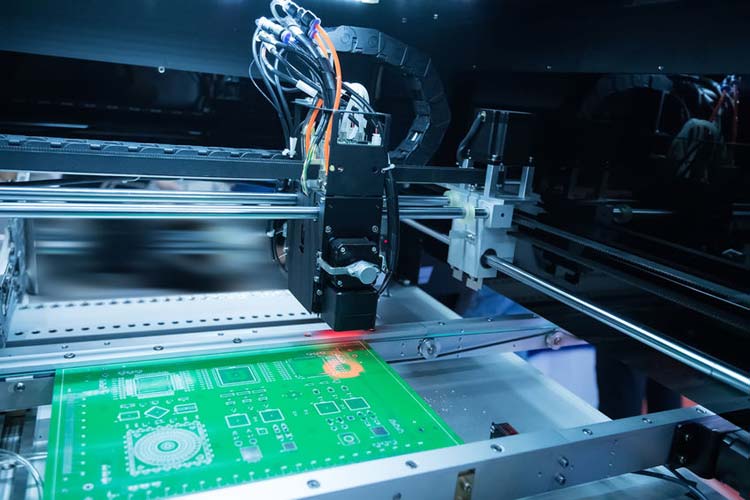

Errors in the manufacturing process of printed circuit boards (PCB) can be very heartbreaking and costly. Such errors mostly are a result of poor design, and they affect the quality of the final product. Manufacturing is among the final phases of PCB development, and this means that a lot of time, materials, and funds have been used so far. Finding out that the PCB cannot be manufactured at this point will be a nightmare, and it will make you ask yourself questions on what could have gone wrong; could it be the layout? The materials?. In this article, we will discuss the guidelines to be followed by designing PCBs that will be manufacturer friendly.
When designing the PCB, you should consider how it is going to be manufactured in order to prevent such costly hiccups. Decisions made during the design phase often have an impact on the costs and the ease of manufacturing the PCB. Design for manufacturing (DFM) involves designing the PCB layout in a manner that is easy to manufacture. The ultimate goal of PCB DFM is to reduce the time and costs of manufacturing. DFM analysis is carried out with the help of software products. You can perform a DFM analysis before handing over the PCB design to the manufacturer so that you can detect and fix any issues that it could have.
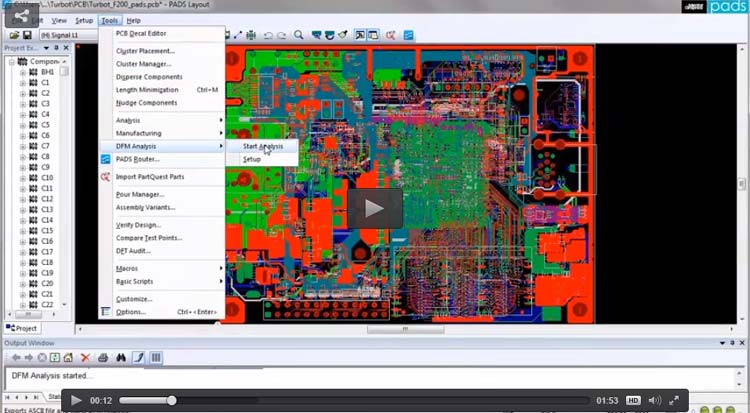
DFM in PCB allows you to address the probable problems early in the design process. PCB problems that may occur during manufacturing as a result of poor design include acid traps, insufficient annular rings, and starved thermal along with many others.
Guidelines for Design For Manufacturing (DFM) in PCB
DFM should start immediately after creating the conceptual design. You should perform every design step with the manufacturing process in mind. You should follow the guidelines below to enable you to achieve the goal of DFM.
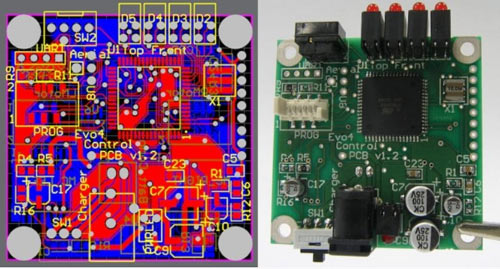
Reduce the number of components on a PCB
Using a minimum number of components reduces the complexity of the board and makes fabrication easier. The increase in the number of parts leads to an increase in the cost of manufacturing. The automation process becomes more complex and expensive with an increase in the number of components.
To reduce the parts, you should go through all of them to determine whether a part can be removed, combined with another, or another component can do its function. The cost of purchasing components i.e low BOM cost and servicing also goes down when their number is reduced. You should invest more in multifunctional components as they help in keeping the numbers at a minimum. Placement of the components on the boards and the soldering process is easier when they are not many. Keeping the components at a minimum generally reduces the cost of manufacturing the PCB.
Modular / Multipurpose Board Designs
Modular design allows both the design and structural versatility hence making the manufacturing process simple. During design, you should consider using small functional blocks that can be used across a range of products. Using the same modules for different products reduces the price per unit when ordering from the manufacturer. Modules also reduce the complexity of fabricating each module.
However, you should plan modules properly, especially when moving the conceptual design to actual design, as it may take more time if not planned well. You should consider all factors, such as where to place some components to optimize space usage and performance.
Use Standard Components
Standard products minimize the risk of error when handling during the manufacturing process. Unique products make manufacturing harder and time consuming as the fabricators are not used to working with them. Additionally, standard components cost less as compared to unique ones. Standard products make the supply chain simple and alleviate quality concerns. Unique components may not be readily available in the market and may become obsolete faster than standard ones.
Avoid Joints and Fasteners Whenever Possible
Threaded fasteners such as washers, nuts, and bolts consume a lot of time as they are difficult to fabricate and automate. Also, it is more costly to use fasteners to mount parts and components than when you use press-fit type mounting techniques. When fasteners cannot be avoided, ensure the standard ones are used, and you can use self-threading screws and captured washers. You should consider using other methods of joining parts, such as using adhesives. The fastening techniques to the materials used, the functional requirements of the product and the manufacturing methods to be used.
Make it Automation Friendly
Automated manufacturing comes with less flexibility as compared to manual manufacturing. You should design the PCB in a way that manufacturing can be done with automation.
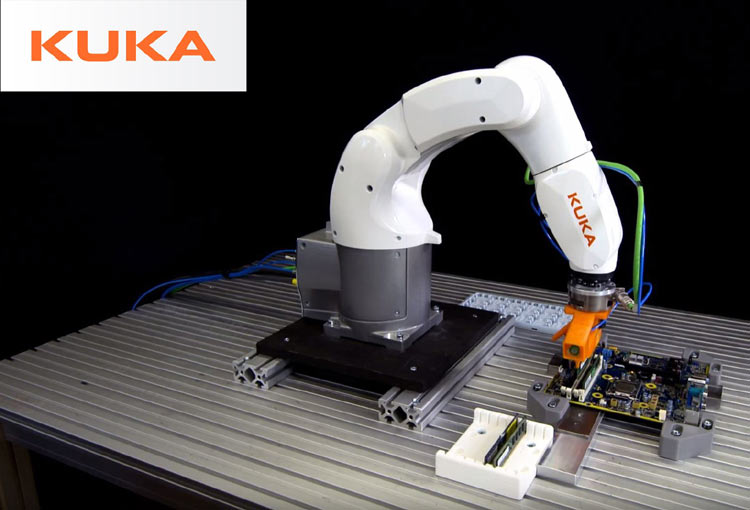

Manufacturing can be automated using two approaches; flexible robotic manufacturing and high speed automated manufacturing. For flexible robotic manufacturing, you should ensure that the design parts use standards grippers. The parts should be self-locating, and simple part-presentation devices should be used. You should ensure that there will be no need to secure some parts as it makes the automation process harder.
With high speed automated manufacturing, you should use a minimum, pre-oriented, and standard parts. Additionally, you should use closed parts, those without projections or slots, to ensure that there is no tangling.
Conclusion
Considering the manufacturing process of the PCB early in the design process, ensure there are no errors in the actual manufacturing process. DFM has many advantages such as cost and time reduction as it eliminates the need for redesign and refabricating by preventing errors in the manufacturing process, use of standard and minimum parts, and the right type of materials that suit the manufacturing process are used.
You should use the list of guidelines, though not exhaustive, given above to ensure that the manufacturing process uses minimal time. DFM also makes automating the manufacturing process easier. Most manufacturers carry out DFM checks before the start the manufacturing process but do not share with the designer any corrective measure they might make. For this reason, you should carry out the DFM checks at the end of the design process.







Comments