Single-Sided vs. Double-Sided PCBs: Which One Is Right for Your Project?
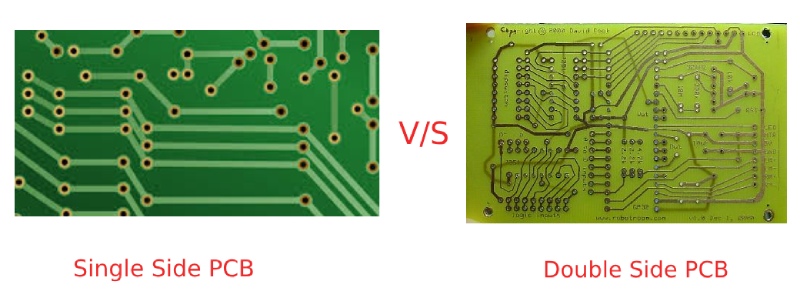
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, enabling the seamless connection of components in a compact and organized way. When it comes to choosing the right PCB for your project, one of the first decisions is whether to go with a single-sided PCB or a double-sided PCB. In this article, we’ll break down the differences, advantages, and ideal use cases for each type to help you make an informed decision.
What Are Single-Sided PCBs?
Single-sided PCBs have a single layer of conductive material (usually copper) on one side of the board. The other side of the PCB is typically reserved for components.
Key Characteristics of Single-Sided PCBs:
- One conductive layer for signal routing.
- Components are placed only on one side.
- Simplistic and straightforward design.
Advantages of Single-Sided PCBs
- Cost-Effective: Single-sided PCBs are cheaper to manufacture, making them ideal for low-budget projects.
- Easy to Design and Produce: Their simple structure allows for quick design and assembly.
- Ideal for Simple Circuits: Best suited for basic electronic devices where minimal connections are required.
Applications of Single-Sided PCBs
- Household appliances like coffee makers and washing machines.
- Basic lighting systems such as LED strips.
- Toys and simple gadgets.
What Are Double-Sided PCBs?
Double-sided PCBs have two conductive layers, one on each side of the board. Components can be placed on both sides, and the two layers are interconnected using vias.
Key Characteristics of Double-Sided PCBs:
- Conductive layers on both sides for more complex circuitry.
- Vias (small holes) connect the layers for better routing flexibility.
Advantages of Double-Sided PCBs
- Increased Circuit Density: More connections can be accommodated compared to single-sided PCBs.
- Greater Design Flexibility: With components and routing on both sides, designers can create more complex circuits.
- Cost-Effective for Complex Designs: While more expensive than single-sided PCBs, they’re still more economical than multilayer PCBs for moderately complex projects.
Applications of Double-Sided PCBs
- Consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets.
- Industrial equipment and automation systems.
- Power supplies and motor controllers.
Single-Sided vs. Double-Sided PCBs: A Direct Comparison
|
Feature |
Single-Sided PCBs |
Double-Sided PCBs |
|
Layers |
One conductive layer |
Two conductive layers |
|
Cost |
Lower production cost |
Moderate cost |
|
Design Complexity |
Simple |
Medium complexity |
|
Applications |
Basic electronic devices |
Consumer electronics, industrial tools |
|
Component Placement |
One side only |
Both sides |
|
Circuit Density |
Limited |
Higher |
Which PCB Should You Choose for Your Project?
Choosing between single-sided and double-sided PCBs depends on your PCB project requirements. Here’s a quick guide:
-
Choose Single-Sided PCBs If:
- Your circuit is simple, with minimal interconnections.
- You’re working with a tight budget.
- You’re designing basic devices like toys or household appliances.
-
Choose Double-Sided PCBs If:
- Your project requires higher circuit density.
- You need to incorporate more components or complex routing.
- You’re designing advanced devices like consumer electronics or industrial tools.
Examples of Projects
Single-Sided PCB Example: LED Light Panel
A single-sided PCB is perfect for an LED light panel where only a few connections are needed between LEDs and the power source.
Double-Sided PCB Example: Arduino Development Board
An Arduino board uses a double-sided PCB to accommodate the microcontroller, resistors, capacitors, and input/output pins while ensuring all components are interconnected efficiently.
Choosing the right PCB type is crucial for the success of your project. While single-sided PCBs are cost-effective and suitable for simpler designs, double-sided PCBs offer greater flexibility and are ideal for more complex applications. Evaluate your project’s requirements, budget, and complexity to make the best decision.
Whether you're working on a DIY project or designing an industrial solution, understanding the differences between single-sided and double-sided PCBs will guide you toward the right choice







Comments