Understanding the IPC standards for PCB design
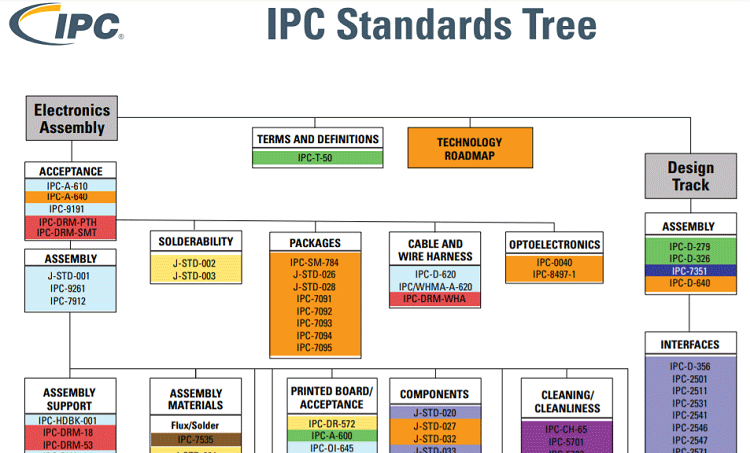
IPC is a trade association that sets the standards and benchmarks for assembling and protecting the electronic equipments. Along with this, it also standardizes the training, market research, and public policy advocacy. The name of this association has been transformed from the Institute of Printed Circuits to Association connecting electronics industries. But still, the acronym “IPC” has managed to retain the label.
IPC is an industry having more than 4000 members who use, specify and design the PCB guidelines in various fields like Automotive, Aerospace, Military, Medical equipment, Telecommunications, etc. These standards are adopted by the electronics industry for designing, manufacturing, and fabricating the PCBs. These standards are should be met at every stage of the production, design, and assembly of a Printed Circuit Board.
History of the IPC standards:
IPC is an association that was founded as a collaboration of six printed circuit board manufacturers in 1957. This association was formed to set the standards for PCB designing and manufacturing. Later in 1977, the name was changed to Interconnecting and packaging electronic circuits. This resulted in the association of more electronic companies with the IPC Association. By 1998, the name was changed as most of the people disagreed with the name and the official name adopted was IPC along with a tagline - Association connecting electronics industries.
Why do the IPC standards matter?
PCB production and designing should be done safely and reliably. Intensive and persistent care is required to manufacture the detailed and committed products. Sticking to the IPC standards would help the companies to maintain PCB standards. Customers prefer the products that are high quality and reliable and thus, for meeting the customer requirements, companies that manufacture the PCBs should commit the quality through the use of IPC standards. When IPC standards are met, the company can improve the processes and quality of the products in various ways.
Benefits of IPC standards
- Improved product quality and reliability: Following the IPC standards in the whole process would help in producing quality products. It will help in enhancing the quality as well as the reliability of the products. This will lead to improved customer satisfaction. IPC standards are also important for improving the consistency of products. This is important to meet the IPC standards for manufacturing reliable and quality PCBs.
- Improved communication: The products that are made by following the IPC standards improvise the communication both internally and externally. Since everyone is using the same terminology and having the same agreements over the expectations from the products. These standards also play an important role in improving communication with customers, supplier vendors, and others. It would be removing the communication delays and inconsistencies.
- Reduced costs: By following the IPC standards, the company needs to lesser resources and thus increasing efficiency. It will diminish the possibility of delays and reworks and thus, reducing the manufacturing costs.
- Improved reputations: Just the name of IPC is enough to get assurance for the product. Someone who gets to know that your business follows the IPC standards will get assured of your commitment and quality about the services. These standards will be opening various opportunities and would make your brand more reputed.

IPC Standard Design Requirements
There is common terminology used to make communication easier and more accurate. There are three classes of products defined by IPC as:
IPC Class 1 PCB Design Requirements: The Class 1 category is for the general electronics products: These are primary requirements for these products are the function of the completed assembly. Generally, everyday products come under this category.
IPC Class 2 PCB Design Requirements: The Class 2 category is for dedicated service electronic products: These products should be highly reliable and should have an extended life. These products may have preferably the uninterrupted services.
IPC Class 1 PCB Design Requirements: The Class 3 category is for High-performance electronic products: This class of the products should provide continuous performance as per the demand. These include the complex and critical systems like the life support systems.
IPC Standard Terminologies
- Acceptance test: These are the tests which are required for determining whether a product is acceptable or not
- Assembly: This term indicates several parts and sub-parts joined together to form one single entity.
- Resist: This term is used for a coating material that protects from the etchant, plating or solder during the manufacturing or the testing of the product.
- Integrated circuit: This indicates the combination of components of a circuit that when interconnected perform a certain function.
- Flexural strength: This term indicates the tensile strength of the outermost fiber of a material that is supposed to bend.
Examples of IPC standards
There are IPC standards for the various process of the manufacturing of PCB. The most commonly used and popular standards are listed below. You can use the official website for more information on each. Do note that IPC standards are not free.
- IPC-2581
- IPC-2221
- IPC-4101C
- IPC-6012B
- IPC-1-600F
- IPC-A-610
- IPC –A-610
- IPC-A-620
IPC standards are required to produce products with high quality. These help in reducing costs and streamline communications.







Comments